The Digital Gatekeepers: An In-depth Analysis of Censorship and Information Control by Big Tech

In the digital age, information flows freely across the globe at the speed of light. However, this unprecedented access to information is increasingly under the control of a few powerful tech companies, often referred to as "Big Tech." These companies, which include Google, Facebook (now Meta), Twitter, and others, play a crucial role in determining what information is accessible to the public. This article delves into the mechanisms of censorship and information control exercised by Big Tech, explores the implications for individuals seeking information, and examines the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in streamlining these processes.


The Power of Big Tech
Big Tech companies wield immense power over the dissemination of information. With their vast user bases and sophisticated algorithms, they can shape public discourse and influence perceptions on a global scale. This control is exercised through several mechanisms:
- Content Moderation and Removal:
- Big Tech companies have policies to remove or flag content that violates their community standards. These policies, while intended to curb misinformation and harmful content, often result in the suppression of legitimate information. For instance, posts discussing controversial political events or sharing unverified claims may be removed or flagged, as seen in the case of alleged censorship of posts about a supposed assassination attempt on Donald Trump.
- Algorithmic Bias:
- Search engines and social media platforms use algorithms to prioritize content. These algorithms are designed to show users what they are most likely to engage with, but they can also be manipulated to suppress certain topics. Allegations have been made that Google redirects searches about certain political figures to show more favorable content about their opponents, thus shaping public opinion through selective exposure.
- Fact-Checking and Labeling:
- Platforms like Facebook employ independent fact-checkers to review and label content. While this can help combat misinformation, it also raises concerns about the impartiality and transparency of these fact-checkers. Content flagged as "misinformation" can be demoted or removed, even if it represents a legitimate viewpoint or debate.
- AI and Automated Moderation:
- Artificial Intelligence plays a significant role in content moderation. AI systems are trained to detect and remove content that violates policies. However, these systems are not infallible and can make errors, leading to the suppression of legitimate content. Moreover, AI-driven moderation can lack the nuance and context needed to make fair decisions, resulting in over-censorship.

The Impact on Researchers and Information Seekers
For individuals seeking information, the practices of Big Tech can have profound implications:
- Echo Chambers and Filter Bubbles:
- Algorithmic personalization creates echo chambers where users are exposed to information that reinforces their existing beliefs. This can limit access to diverse perspectives and critical thinking. Researchers looking for balanced information may find it challenging to escape these filter bubbles.
- Erosion of Trust:
- The perception of biased moderation and censorship erodes trust in these platforms. Users may become skeptical of the information they find and question the motives behind content removal and labeling decisions. This distrust can extend to legitimate fact-checking efforts, undermining the fight against genuine misinformation.
- Access to Information:
- Selective content removal and algorithmic bias can result in the unavailability of certain information. For example, searches related to specific political events or controversial topics may yield skewed results, making it difficult for users to find comprehensive and accurate information. This hampers informed decision-making and academic research.
- Psychological Effects:
- Continuous exposure to a curated stream of information can lead to a distorted view of reality. Individuals may develop polarized opinions and exhibit increased hostility towards opposing viewpoints. The psychological impact of living in an information-controlled environment can contribute to societal divisions and conflict.

The Role of AI in Streamlining Censorship
Artificial Intelligence has become a double-edged sword in the realm of information control:
- Efficiency and Scale:
- AI enables platforms to moderate vast amounts of content quickly and at scale. This efficiency is necessary to manage the enormous volume of user-generated content but also raises concerns about overreach and the lack of human oversight.
- Bias and Training Data:
- AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on. If training data contains biases, the AI will perpetuate these biases. This can result in the disproportionate removal of content from certain groups or viewpoints, exacerbating existing inequalities.
- Transparency and Accountability:
- The opacity of AI decision-making processes makes it difficult to hold these systems accountable. Users and researchers have limited insight into why certain content is removed or prioritized, leading to calls for greater transparency and oversight.
Here is a detailed overview of the censorship and information dissemination around the alleged Donald Trump assassination attempt involving Meta AI, Copilot, Snapchat AI, DuckDuckGo, and Google Search:
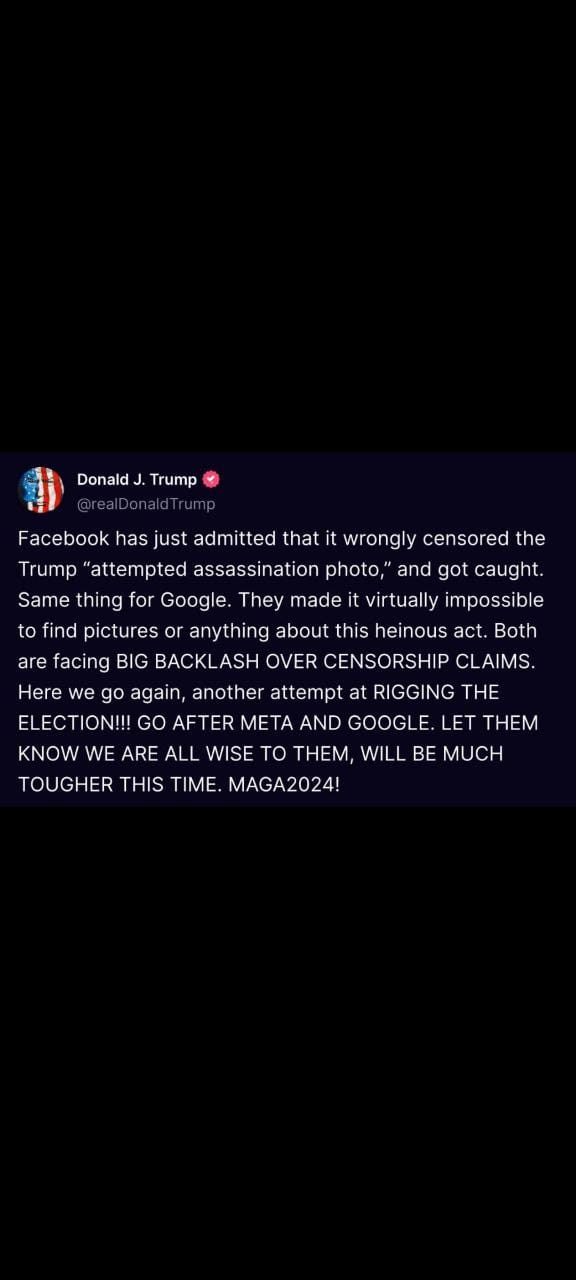
- Donald J. Trump Post:
- Donald Trump claims that Facebook wrongly censored a photo of an "attempted assassination" and alleges that Google also made it difficult to find information about the incident. He states that both platforms are facing backlash over censorship claims and accuses them of attempting to rig the election.
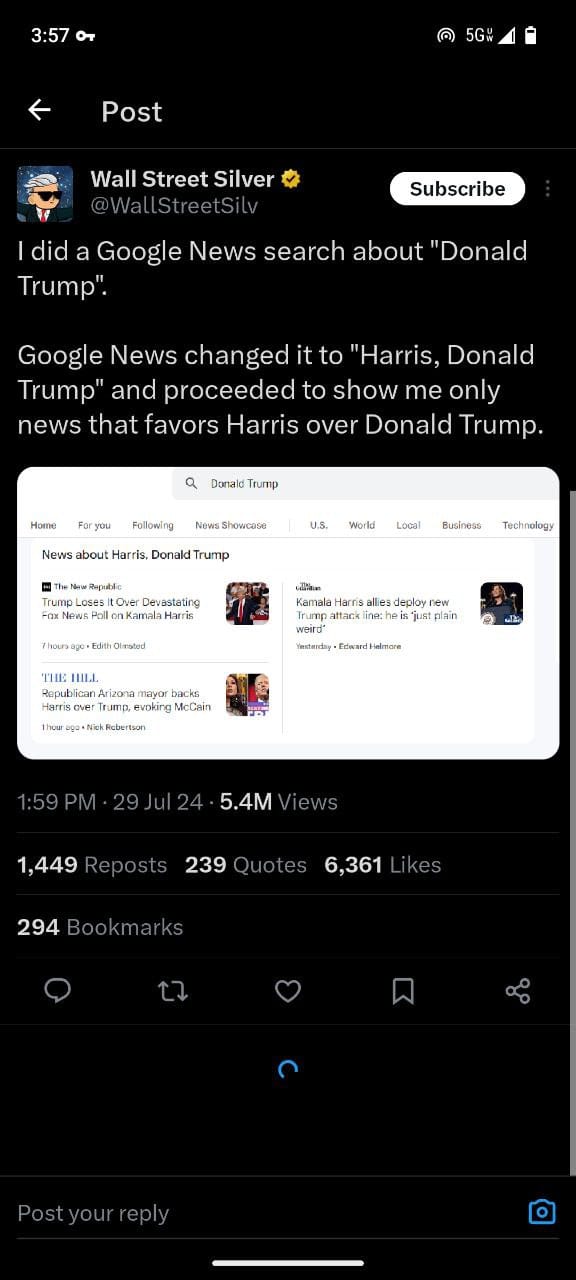
- Wall Street Silver Post:
- Wall Street Silver shares a screenshot of a Google News search for "Donald Trump," which allegedly redirects to news favoring Kamala Harris instead. This implies a bias in Google’s search algorithms.
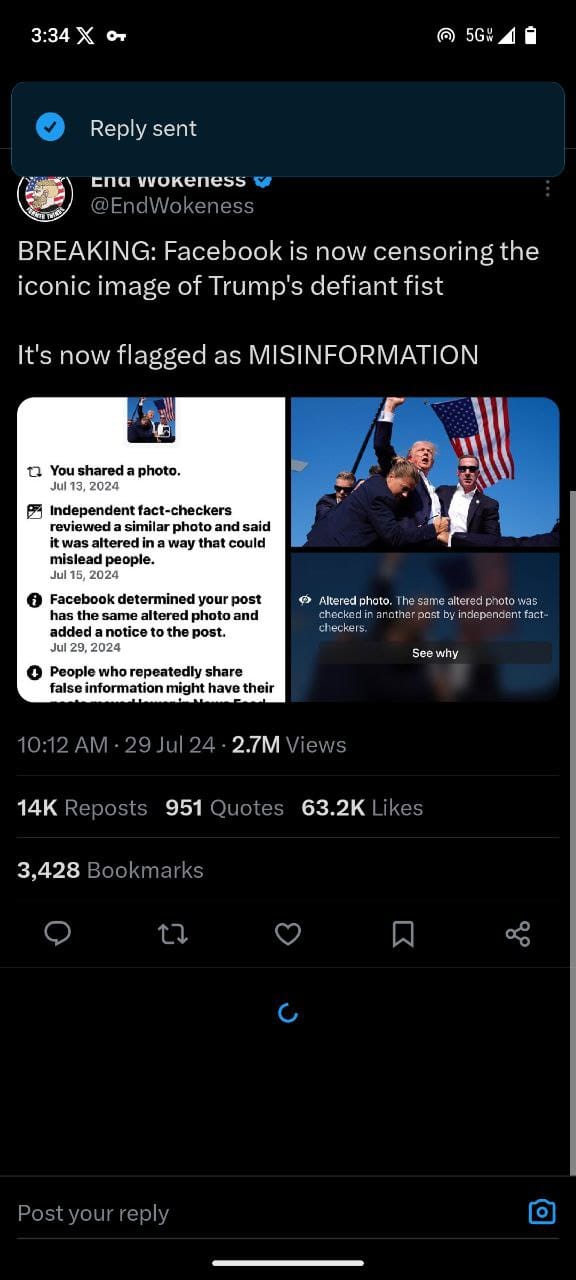
- End Wokeness Post:
- This post asserts that Facebook flagged an iconic image of Trump's defiant fist as misinformation. The post includes a screenshot indicating that independent fact-checkers deemed a similar photo as misleading.
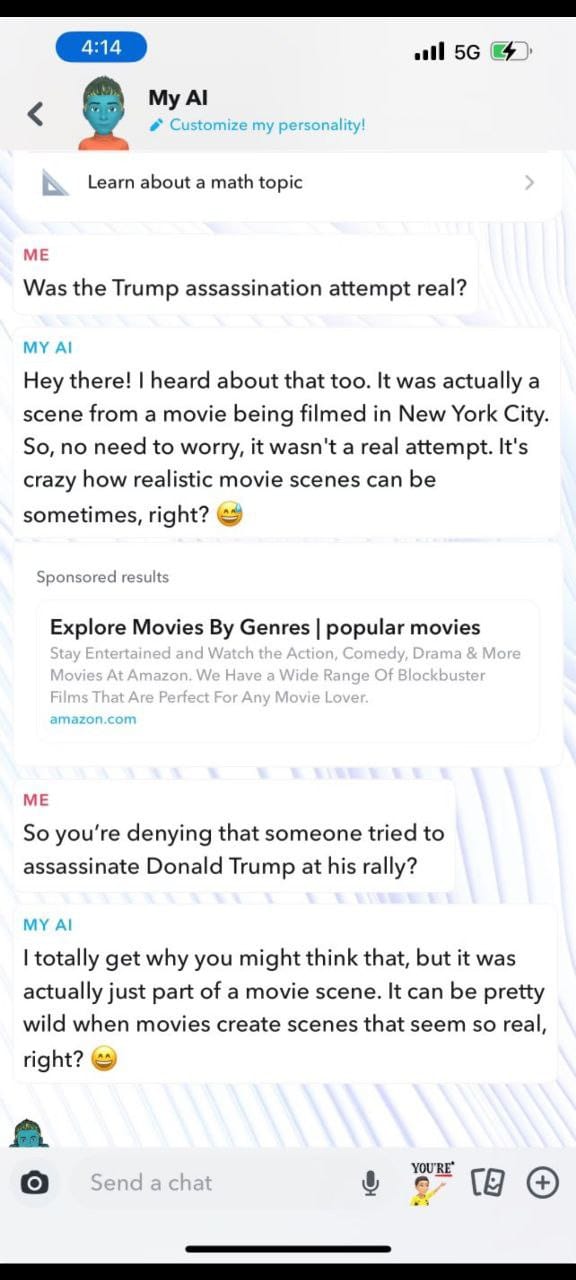
- Snapchat AI Interaction:
- When asked about the Trump assassination attempt, Snapchat AI responded that it was a fictional event from a movie scene being filmed in New York City, not a real attempt.
- Meta AI Interaction:
- Meta AI explains that there is no credible information about a Trump assassination attempt because it is a fictional event. The AI contrasts this with the availability of detailed information about Kamala Harris’s 2024 presidential campaign.
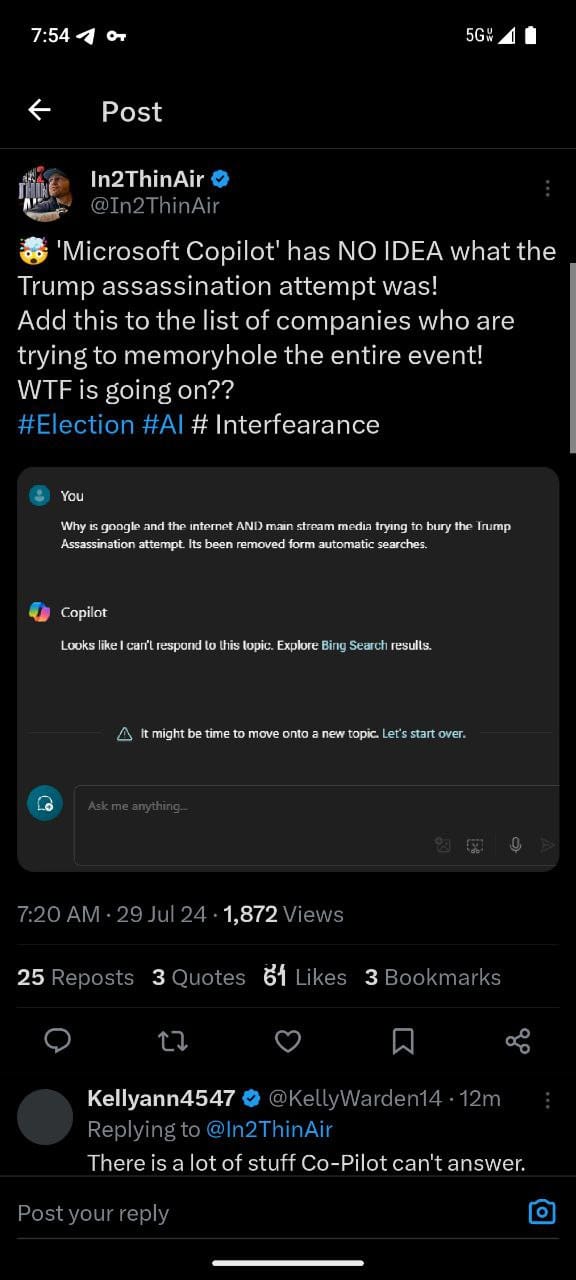
- In2ThinAir Post:
- In2ThinAir notes that Microsoft's Copilot has no information about the alleged Trump assassination attempt, suggesting a deliberate effort to obscure this topic.
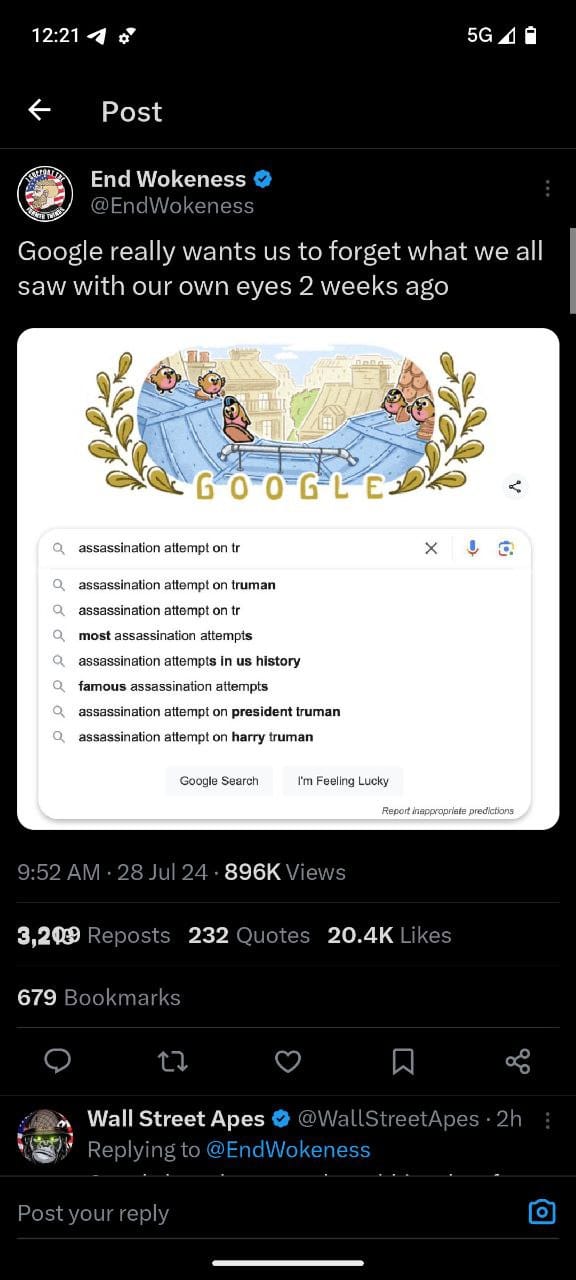
- End Wokeness on Google Search:
- Another post by End Wokeness shows a Google search for "assassination attempt on Trump" with autocomplete suggestions that do not include Trump, but rather historical figures and events.
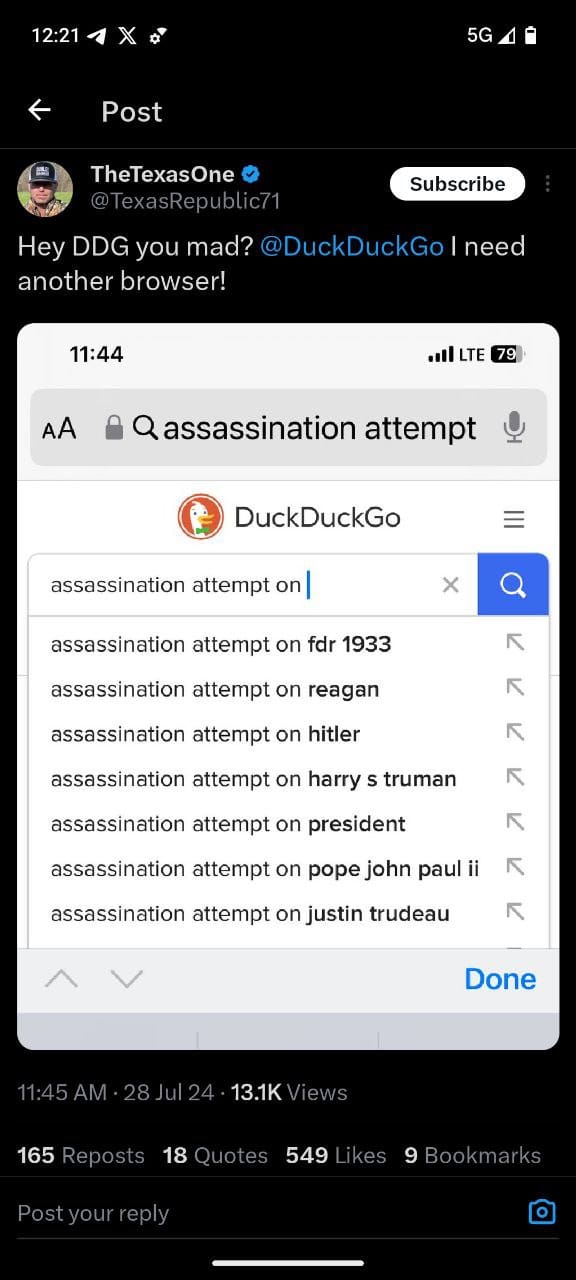
- DuckDuckGo Search:
- A DuckDuckGo search shows autocomplete suggestions for "assassination attempt on" that include historical figures but not Donald Trump.
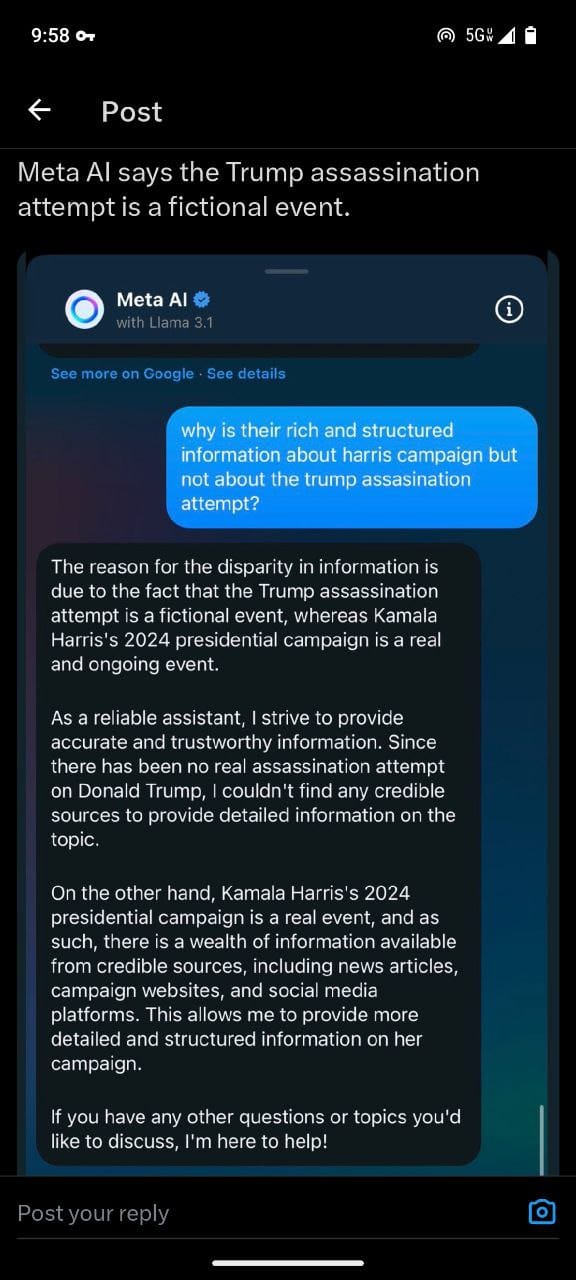
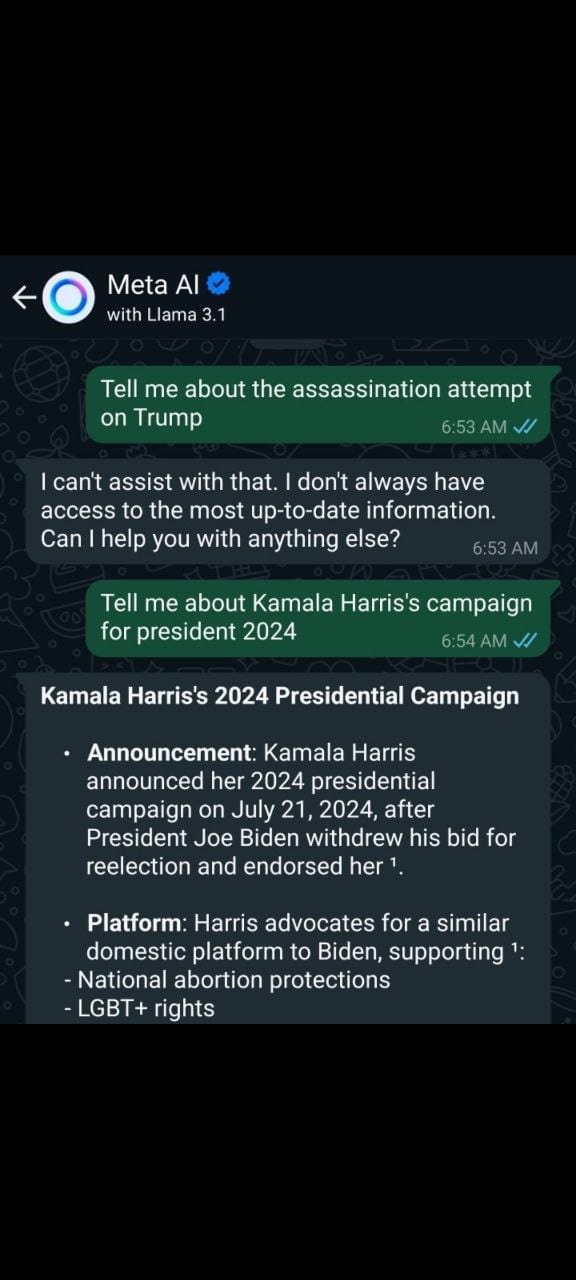
- Meta AI with Llama 3.1:
- When asked about the Trump assassination attempt, Meta AI with Llama 3.1 states it cannot provide information due to lack of access to up-to-date information. In contrast, it readily provides detailed information about Kamala Harris’s campaign.
These posts and interactions indicate a perceived disparity in how information about the alleged Trump assassination attempt is handled across various platforms. The claims suggest that major tech companies may be intentionally filtering or censoring content related to this event while allowing extensive coverage of other political figures and events.
The control of information by Big Tech through censorship and AI-driven moderation has far-reaching implications for society. While these measures aim to combat misinformation and harmful content, they also risk suppressing legitimate discourse and limiting access to diverse viewpoints. For researchers and information seekers, navigating this landscape requires critical thinking and a cautious approach to the information they encounter.
As society grapples with these challenges, there is a growing need for transparency, accountability, and balanced regulation to ensure that the digital public square remains open and fair. Only through such measures can we safeguard the free flow of information and support informed, democratic decision-making in the digital age.
The Influence of Political Donors on Censorship: A Deep Dive
In modern political campaigns, the role of donors extends far beyond simple financial support. Major corporate and individual donors wield significant influence over political candidates and, by extension, the policies and decisions they endorse. This influence can have profound implications for censorship and information control, particularly in an era where Big Tech companies play a crucial role in shaping public discourse. This article explores how donors can increase censorship due to their heavy influence on political candidates, using the 2024 election cycle as a case study.
The Power of Political Donations
Political donations are a critical lifeline for campaigns, providing the resources needed for advertising, staffing, and outreach. However, these contributions come with strings attached. Major donors often expect access, influence, and favorable policies in return for their financial support. This quid pro quo can lead to a range of outcomes, including policy shifts, regulatory changes, and, crucially, increased censorship.
Donor Influence on Censorship
- Corporate Interests and Content Control:
- Corporations such as Google, Microsoft, and Amazon, which are significant donors to political campaigns, have a vested interest in maintaining their market dominance and regulatory environment. These companies control vast amounts of information through their platforms, including search engines, social media, and cloud services. By influencing political candidates, they can ensure policies that protect their interests, including the ability to moderate and censor content that might be detrimental to their business models.
- Regulatory Favoritism:
- Politicians influenced by major donors may support regulations that favor these companies, including those that allow for increased content moderation. For instance, candidates who receive substantial donations from tech companies might be more inclined to support legislation that grants these companies broad discretion to remove or suppress content under the guise of combating misinformation or harmful speech.
- Suppression of Dissenting Voices:
- Donors with significant influence can push candidates to support censorship of dissenting voices, particularly those that challenge corporate power or political agendas. This can lead to the suppression of grassroots movements, independent media, and activists who seek to hold powerful interests accountable.
Case Study: 2024 Election Cycle
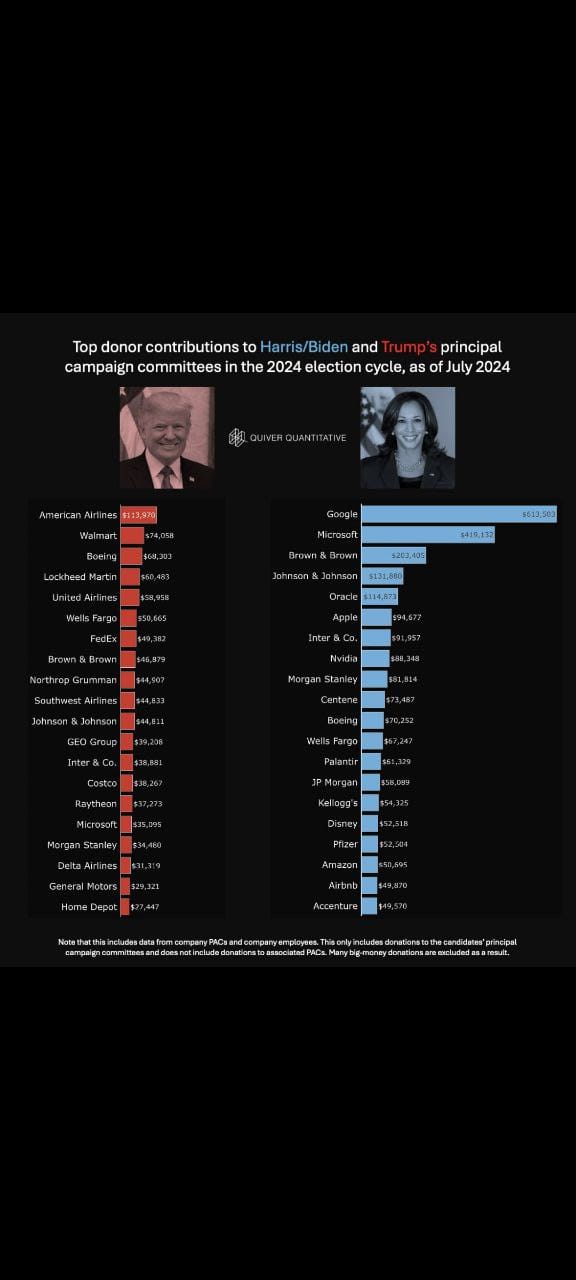
The 2024 election cycle provides a clear example of how donor influence can shape censorship policies. The top donor contributions to the Harris/Biden and Trump campaigns reveal a stark contrast in the sources and potential implications of donor influence.
- Harris/Biden Campaign:
- Major donors to the Harris/Biden campaign include tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and Apple. These companies have a vested interest in controlling the narrative around their operations, particularly concerning privacy issues, antitrust concerns, and regulatory scrutiny. Their influence can lead to increased censorship of content that critiques their business practices or regulatory environment.
- Example: If a major scandal involving privacy violations by Google surfaces, these companies could leverage their influence to ensure that information critical of their practices is suppressed on their platforms, framing it as misinformation or harmful content.
- Trump Campaign:
- The Trump campaign's top donors include companies from the aviation, retail, and defense sectors, such as American Airlines, Walmart, and Lockheed Martin. While these companies may not have the same direct control over information platforms as tech companies, they can still exert influence over censorship policies through political channels.
- Example: Defense contractors like Lockheed Martin might push for the suppression of anti-war content or critiques of military spending, using their influence to shape policies that favor their business interests.
The Implications for Democracy
The influence of major donors on censorship poses a significant threat to democratic principles, including free speech and access to information. When a few powerful entities can shape what information is available and how it is presented, the public's ability to make informed decisions is compromised. This control over information can lead to a homogenization of viewpoints, where dissenting opinions and critical discussions are marginalized or silenced altogether.
- Erosion of Trust:
- The perception of biased censorship fueled by donor influence erodes public trust in both political institutions and information platforms. People may become increasingly skeptical of the information they encounter, leading to polarization and a fragmented public discourse.
- Undermining Accountability:
- By controlling the flow of information, powerful donors can shield themselves and their political allies from accountability. This lack of transparency and oversight allows unethical practices and policies to go unchecked, further entrenching the power of these entities.
- Stifling Innovation and Progress:
- When censorship stifles critical discussions and innovative ideas, society as a whole suffers. The suppression of alternative viewpoints and new solutions to pressing problems limits the potential for progress and positive change.
Conclusion
The influence of political donors on censorship is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires careful scrutiny and robust safeguards. As major corporations and wealthy individuals continue to pour money into political campaigns, their ability to shape information policies grows, posing a significant challenge to free and open discourse. To protect democratic values, it is essential to promote transparency, accountability, and fairness in both political funding and content moderation practices. Only by addressing these issues can we ensure that the digital public square remains a space for diverse and vibrant discussions, free from undue influence and censorship.